1. Introduction to State Management:
Understanding State in React:
State refers to data that can change over time within a component.
Components can have local state, which is managed within the component itself.
State is essential for building dynamic and interactive user interfaces.
Stateful vs. Stateless Components:
Stateful components (also known as Class components or Components with state) manage their own state using the
setStatemethod.Stateless components (also known as Functional components) do not have internal state and receive data via props.
Importance of Effective State Management:
Effective state management ensures that data is consistent and up-to-date across components.
It helps in building scalable and maintainable React applications by organizing and managing data efficiently.
16 Context API :
The Context API in React allows you to share data across components without having to pass props manually, providing a centralized way to manage state in your application.
Purpose: Manages state for multiple components without prop drilling.
Centralized State: Creates a central store of data accessible anywhere in the component tree.
Provider-Consumer Model: Provider supplies data, consumers access it.
Creating Context: Use
createContext()to make a new context object.Provider Component: Wraps part of the tree and provides data via
valueprop.Consumer Component: Accesses data from nearest Provider using render prop or
useContexthook.useContext Hook: Simplifies consuming context in functional components.
Updating Context: Changes in Provider trigger re-renders in consuming components.
Performance: Be cautious with deeply nested trees or frequent updates.
Redux Alternative: Can replace Redux for simpler state management.
Limitations: May not be suitable for all scenarios, especially complex state or performance-critical apps.
Implementing Context API in a Next.js Application
0. File Structure:
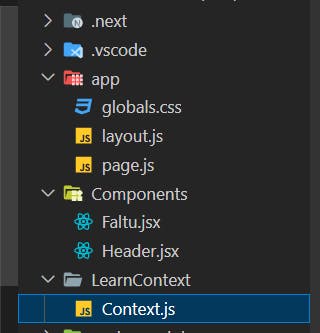
1. Create a Context File:
File Name: Context.js
"use client"; // This line seems unnecessary and might be a placeholder or comment. It doesn't affect the code.
import React, { createContext, useState } from 'react'; // 🎯 Import necessary modules
export const MyContext = createContext(); // 🎯 Create a context named MyContext
const Context = ({ children }) => { // Define a component named Context, which takes children as props
const username = 'Ayush- MERN Stack Developer'; // Define a variable username
const roll = 49; // Define a variable roll
const [user, setUser] = useState('Ayush - MERN Stack Developer'); // Define state variables user and setUser using useState hook
return (
<>
{/* <MyContext.Provider value={username} > */}
{/* <MyContext.Provider value={[username, roll]} > */}
<MyContext.Provider value={{ user, setUser }} > {/* 🎯 Provide the context with value of user and setUser */}
{children} // Render children components within the context provider
</MyContext.Provider>
</>
)
}
export default Context; // Export the Context component as default
2. Wrap Your Next.js App with the Provider:
File Name: layout.js
import "./globals.css"; // Import global CSS styles
import { MyContext } from "@/LearnContext/Context"; // 💀❌🚨
import MyContext from "@/LearnContext/Context"; // 🎯 Import the MyContext component from Context.js
export const metadata = { // Metadata object containing title and description
title: "Create Next App",
description: "Generated by create next app",
};
export default function RootLayout({ children }) { // Define a component named RootLayout which takes children as props
return (
<html lang="en"> {/* HTML tag with language set to English */}
<body> {/* Body tag */}
<MyContext> {/* 🎯🎯 Use MyContext as a wrapper */}
{children} {/* Render children components within MyContext */}
</MyContext>
</body>
</html>
);
}
3. Consume Context in Components:
File Name: Faltu.js
import { MyContext } from '@/LearnContext/Context'; // Import the MyContext context from Context.js
import React, { useContext } from 'react'; // 🎯 Import necessary modules
const Faltu = () => { // Define a component named Faltu
// const user1 = useContext(MyContext); // Use useContext hook to access the context and assign it to user1
// const [user2, roll2] = useContext(MyContext); // Use useContext hook to access the context and destructure user2 and roll2 from it
const { user, setUser } = useContext(MyContext); // 🎯 Use useContext hook to access the context and destructure user and setUser from it
return (
<>
{/* <p>Faltu Page: {user1}</p> Display user1 obtained from context */}
{/* <p>Faltu Page: {user2}, and roll: {roll2} </p> Display user2 and roll2 obtained from context */}
<p>Faltu Page: {user} </p> {/* Display user obtained from context */}
</>
)
}
export default Faltu; // Export the Faltu component as default
4. Update Context Data:
File Name: Header.js
import { MyContext } from '@/LearnContext/Context'; // Import the MyContext context from its file
import React, { useContext } from 'react'; // Import necessary modules
const Header = () => { // Define a component named Header
// let user = useContext(MyContext); // Access the user value from the context using useContext hook
// let [user, roll] = useContext(MyContext); // Use useContext hook to access the context and extract user and roll variables
let { user, setUser } = useContext(MyContext); // 🎯 Access both user and setUser from the context using destructuring
return (
<>
<button className='my-btn' >{user}</button> {/* Render a button displaying the user value */}
<button onClick={() => setUser('New Name- Rahul')} className='my-btn bg-orange-500' >Update- Username</button> {/* Render a button to update the user value */}
</>
)
}
export default Header; // Export the Header component as default
Redux
