tryblock:Encloses code that might throw an error.
Code inside the
tryblock is executed.If an error occurs, control jumps to the
catchblock.
catchblock:Handles errors thrown in the corresponding
tryblock.Allows graceful error handling without crashing the script.
Can specify the type of error to catch or catch any error.
Example of Try-Catch Block in JavaScript for Error Handling
// Simple try-catch block to handle potential errors
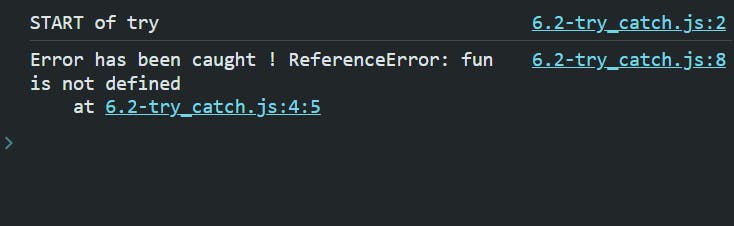
try {
console.log("START of try");
// blablabla; // Placeholder for potential code that might throw an error
fun(); // Calling function 'fun' which might throw an error
console.log("End of try");
} catch (err) {
console.log("Error has been caught !", err); // Log any caught errors
}
⛔Error Handling with setTimeout:
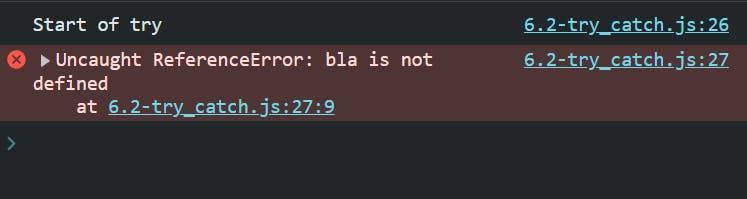
try {
// Execute the following code after a delay of 2000 milliseconds (2 seconds).
setTimeout(function () {
// This code will be executed after the delay.
console.log("Start of try");
// An error will be thrown here because 'bla' is not defined.
bla;
// This line will not be executed due to the error above.
console.log("END of try");
}, 2000);
} catch (err) {
// If an error occurs within the try block, it won't be caught here.
// This catch block is not relevant to the error inside setTimeout.
console.log('Outer of setTimeout', err);
}
This code doesn't work as expected because the error thrown inside the setTimeout callback function is not caught by the catch block outside of the setTimeout.
Here's why:
When you use
setTimeout, the callback function is executed asynchronously after the specified delay (in this case, after 2000 milliseconds).The
tryblock doesn't wait for the asynchronous operation (in this case,setTimeout) to complete before moving to thecatchblock. As a result, any errors thrown inside thesetTimeoutcallback are not caught by the surroundingtry...catchblock.
✅ Correct way - To handle errors thrown inside asynchronous operations
To handle errors thrown inside asynchronous operations like setTimeout, you need to place the try...catch block inside the callback function itself. This way, you can catch errors that occur within the asynchronous operation:
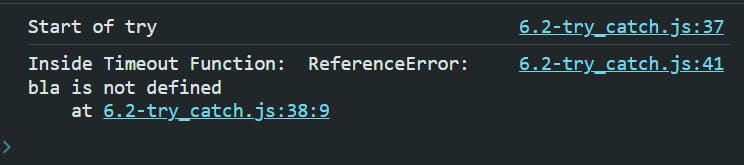
// Set up a delayed execution using setTimeout.
setTimeout(function () {
// Inside the setTimeout function, set up a try-catch block to handle potential errors.
try {
console.log("Start of try");
// An error will be thrown here because 'bla' is not defined.
bla;
console.log("END of try");
} catch (err) {
// If an error occurs within the try block, it will be caught here.
console.log("Inside Timeout Function: ", err);
}
}, 2000);
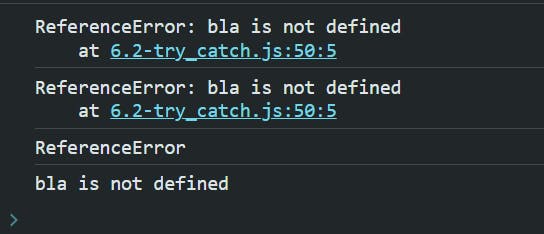
Accessing error properties
try {
// Code that might throw an error
bla;
} catch (err) {
// Accessing error properties
console.log(err.name); // Output: "ReferenceError"
console.log(err.message); // Output: "bla is not defined"
console.log(err.stack); // Output: Stack trace information
}
JSON Parsing and Stringifying
try {
// Define a JSON string.
// let myJson = `{"name": "John","age": 25}`;
let myJson = '{"name": "John","age": 25}';
console.log(myJson); // Output: {"name": "John","age": 25}
console.log(typeof myJson); // Output: string
// Parse the JSON string into an object.
let user = JSON.parse(myJson);
console.log(typeof user); // Output: object
console.log(user); // Output: { name: 'John', age: 25 }
console.log(user.name); // Output: John
console.log(user.age); // Output: 25
// Convert the object back to a JSON string.
let phirJSON = JSON.stringify(user);
console.log(phirJSON); // Output: {"name":"John","age":25}
console.log(typeof phirJSON); // Output: string
// if (!user.address) {
// throw new Error('User must have a address'); // ⚠️ Error: User must have a address
// }
} catch (err) {
// Catch and log any errors that occur during JSON parsing or stringifying.
console.log(err);
}
try-catch-finally Blocks - Error Handling
try {
// Code that may throw an error
console.log("Inside try block");
throw new Error("An error occurred");
} catch (error) {
// Catch block to handle any errors
console.error("Caught an error:", error.message);
} finally {
// Finally block will always execute, regardless of whether there's an error or not
console.log("Inside finally block");
}
